Increased Lifetime
TTG
Targeted equal force in the thread area
TTG, a patented manufacturing process for creating threads in nuts or on bolts ensures optimum fitting accuracy in the thread when tightened. This innovative method not only enhances durability but also enables bolts with TTG to withstand significantly higher loads. Consequently, the connection diameter can be reduced, leading to substantial material savings. Threads featuring TTG revolutionize connection possibilities and offer cost-saving benefits.
The task of a bolt is to connect two or more components. This happens due to the axial bolt pretensioning force. But what is the axial pretensioning force? What is a thread? Basically, a thread is a sloping level which is wound up. If you screw a nut on the bolt thread, it follows this sloping level – the flank lead. When the nut reaches the flange you generate bolt elongation and flange compression by further screwing. This bolt elongation is the aforesaid pretensioning force and is a result of the stretched bolt material. Taking a close look at the pretensioning force generation, usually it has impact on the nut due to a torque. This equals a torsional stress on the bolt, which works against the bolt in its actual function. That is the reason why Bolt Tensioners, Hydraulic Nuts and Multiple Stud Nuts are used, which do nothing else than pretensioning the bolt purely axial and torsion-free.
In general although, any pretensioning force generation does not only elongate the bolt shaft, but also the thread. A distortion of the heavily loaded thread occurs, which does not comply with the original geometry of the nut anymore.
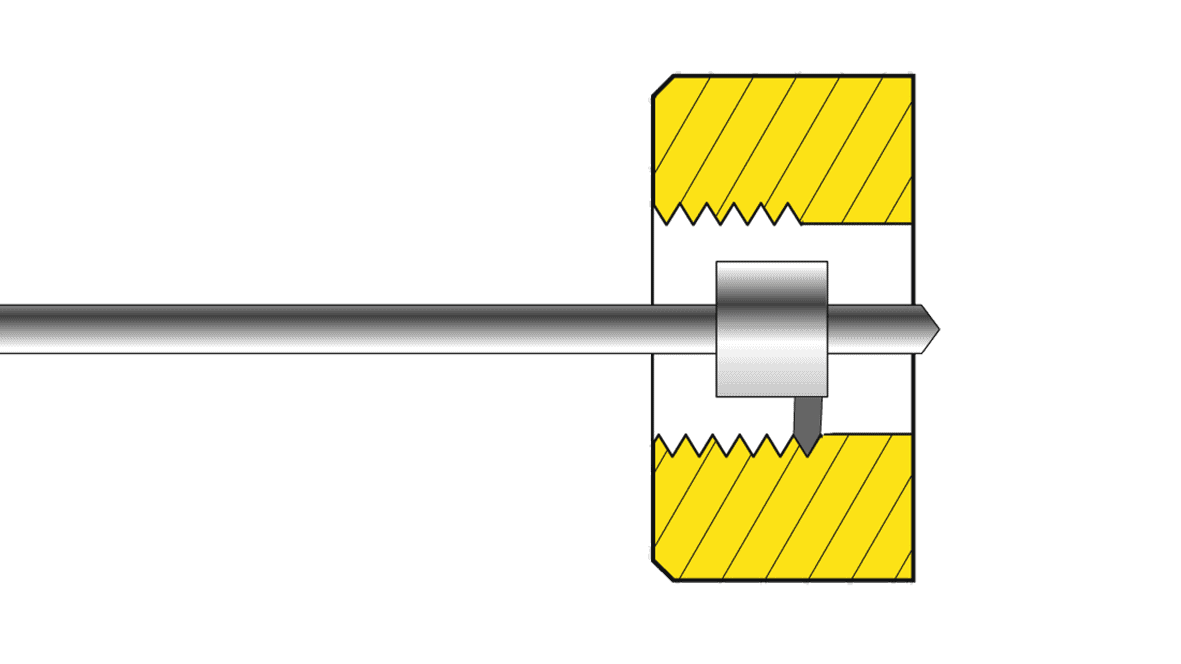
The patented idea of SCHAAF GmbH & Co. KG is to copy the profile of the highly pretensioned bolt thread in the nut area and to transfer it to the nut with the exact change of geometry.
What is the result? The whole flank surface of the bolt has an equally exact contact with the nut with TTG thread. Therefore, there is no stress concentration as before in the first thread turns where nut and bolt touch. Instead, the pretensioning force distributes equally over the complete geometry. Highly stressed threads, which are mostly charged with additional dynamic load, receive a higher longevity, higher safety at same component size and with insignificant higher costs.






Take a picture of pretensioned bolt
Determination of thread geometry
Manufacturing the nut after determination
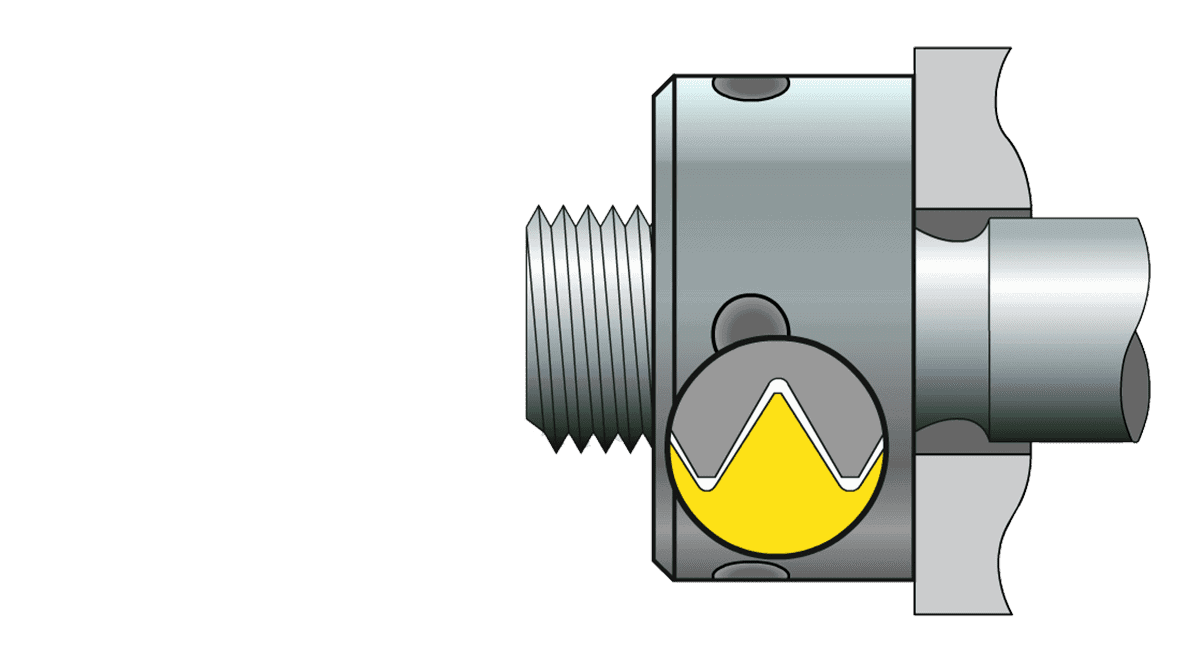
Flank contact at untensioned bolt
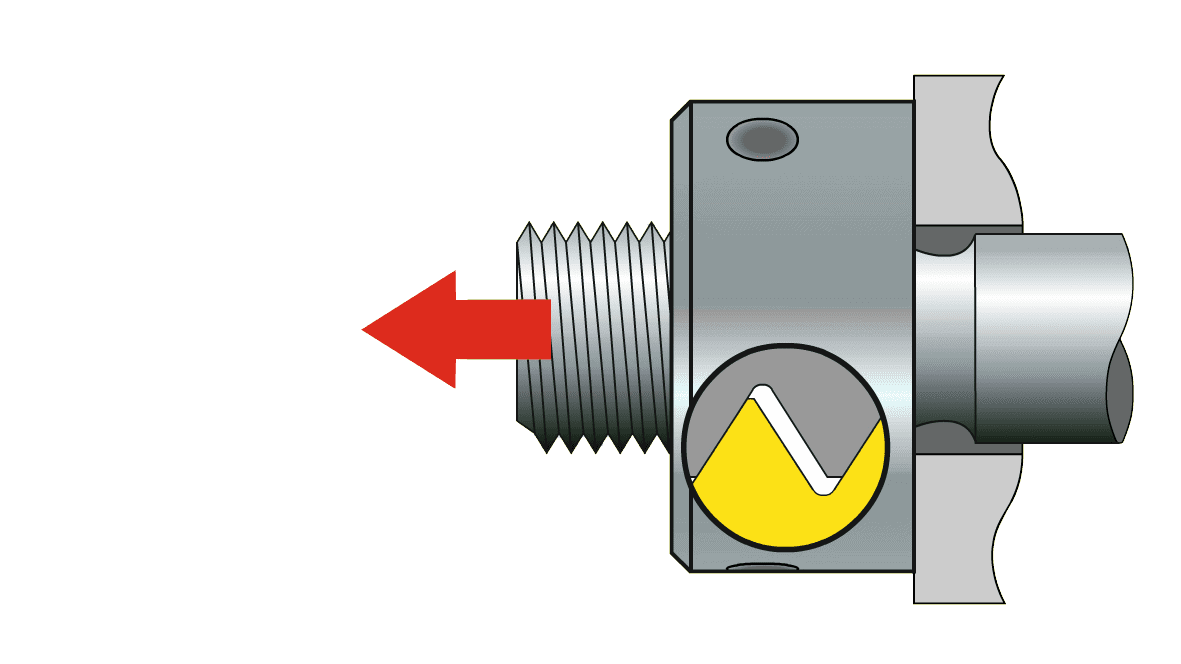
100% flank contact with targeted equal force on the pretensioned bolt...
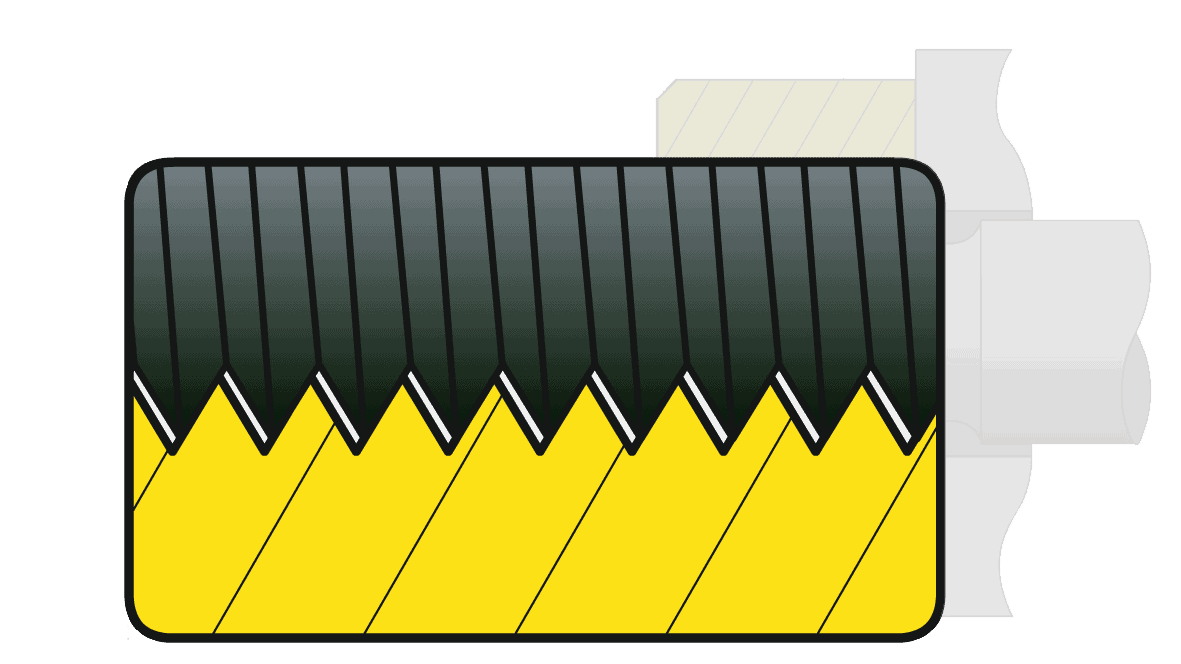
... over the complete area
Advantages
- Nut and bolt flanks have a 100 % contact at the pretensioning force and the load distributes equally on the complete thread bearing surface
- The permanent risk of fracture with highly stressed connections is significantly decreased
- Bolt fractions in the first thread turn can be avoided
- Low costs
- More resilient connections
- Higher machine safety
- Due to geometry displacements, tension launching is even possible in the upper part of the nut
- Due to nuts with TTG, bolts with the identical cross sections can be stressed, respectively pretensioned higher. The connection becomes safer
- TTG is independent of the nut material
- TTG improves every bolt connection
Proven security
The TTG patented by SCHAAF has been extensively tested in several test procedures by the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft as part of its technology research and has been awarded internationally valid certificates.
Results of the fatigue tests
Highest potential for the hot-dip galvanized stud bolts with TTG nuts in terms of their fatigue strength
The typical fatigue failure (breakage in the first thread turn) proven
TTG nut changes the force flow in the thread and increases the service life
Tests show that with the hot-dip galvanized TTG-Sets a higher fatigue strength could be achieved compared to HV
The use of stud bolts with SCHAAF TTG nuts allows for enormous optimisations
Stud bolts with smaller nominal diameters can be used, which leads to lower eccentricities and smaller flange dimensions
The lower eccentricities cause less additional bending loads on the stud bolt, which also has a positive effect on the service life of the connection
High savings potentials are expected for future flange dimensions


MEDIA AND MORE
















